Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Researchers Find New Way to Slow Memory Loss in Alzheimer’s
COLD SPRING HARBOR, N.Y., Feb. 05, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) --
Alzheimer’s disease is often measured in statistics: millions affected worldwide, cases rising sharply, costs climbing into the trillions. For families, the disease is experienced far more intimately. “It’s a slow bereavement,” says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Nicholas Tonks, whose mother lived with Alzheimer’s. “You lose the person piece by piece.”
There’s a lot of discussion about how the neurodegenerative disorder may be caused by a buildup of “plaque” in the brain. When someone refers to this plaque, they’re talking about amyloid-β (Aβ), a peptide that occurs naturally but can accumulate and come together. This is known to promote Alzheimer’s disease development.
Now, Tonks, graduate student Yuxin Cen, and postdoctoral fellow Steven Ribeiro Alves have discovered that inhibiting a protein called PTP1B improves learning and memory in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model.
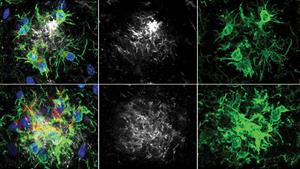
Tonks discovered PTP1B in 1988 and has studied this enzyme’s implications for health and disease ever since. In this latest study, his team shows how PTP1B directly interacts with another protein called spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK), which normally regulates microglia (the brain’s immune cells) to clear out debris like excess Aβ. “Over the course of the disease, these cells become exhausted and less effective,” says Cen. “Our results suggest that PTP1B inhibition can improve microglial function, clearing up Aβ plaques.”
Beyond Aβ, obesity and type 2 diabetes are well recognized risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and are believed to contribute to its increasing prevalence worldwide. These links provide additional rationale for going after PTP1B in Alzheimer’s disease, as it’s a validated therapeutic target for both metabolic disorders.
Newly approved therapies for Alzheimer’s disease primarily focus on targeting Aβ clearance, yet offer only modest clinical benefits for many patients. “Using PTP1B inhibitors that target multiple aspects of the pathology, including Aβ clearance, might provide an additional impact,” says Ribeiro Alves.
The Tonks lab is currently working with DepYmed, Inc. to develop PTP1B inhibitors for multiple applications. For Alzheimer’s disease, Tonks envisions a combination of therapies that pair existing approved drugs along with PTP1B inhibitors. “The goal is to slow Alzheimer’s progression and improve quality of life of the patients,” he says. With this research establishing PTP1B as a potential therapeutic target for the disease, it may hold the key to doing just that.
ABOUT COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY:
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory is one of the world's most renowned institutions for biomedical research and education located on the North Shore of Long Island. Founded in 1890 and home to eight Nobel laureates, the 501(c)(3) nonprofit inspires curiosity, discovery, and innovation in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology, and artificial intelligence, including new treatments for breast cancer, spinal muscular atrophy, and other life-threatening diseases. For more information, visit www.cshl.edu.
Contact:
Gina DiPietro
dipietro@cshl.edu
A photo accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/9bc26723-d9f6-460f-b5d7-7869f7bbe403

Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.